Manufacturing involves producing parts in high volumes to save time and meet increased demands. Injection molding is one of the cost-efficient processes used in manufacturing to produce these parts. Unlike other types of machining, injection molding is efficient since it reduces material wastage, and the overall cost per part is lower. Although it's mostly used for plastic parts, it's also ideal for producing other materials such as metal. Here are the details to help you understand the basics of the process.
How Injection Molding Works
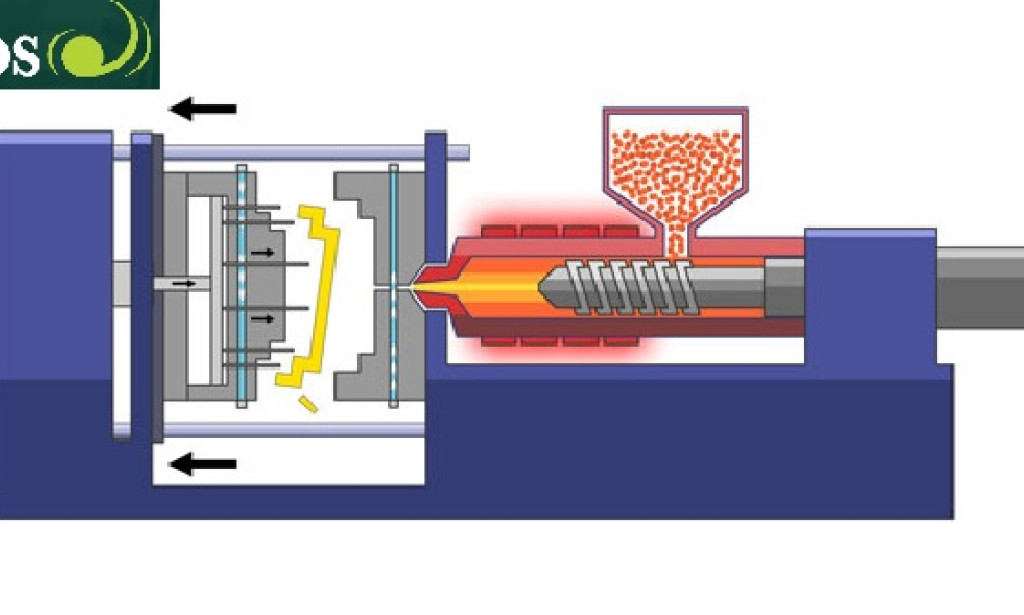
Injection molding involves pouring molten material into a desired shape molt cavity where it cools and solidifies. The process may vary depending on the type of molding. But the typical process involves the following steps.
-
Molting: the first step is to mill the material into small pellets to make it easier to molten. Once the pellets are ready, they're loaded into a barrel on the injection molding machine. The temperatures are increased until the pellets melt and compress.
-
Injection: This involves injecting the molten material into a mold cavity of the desired shape. Ideally, the material should fill all the mold cavity parts for a perfect product. Then, a screw or plunger forces the material into the cavity.
-
Cooling: The material is left to cool and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold cavity. The heat dissipates through a cooling fluid running through the cavities' cooling channels.
-
Ejection: Once the mold has completely cooled, it means the part is ready. The cavity opens, and the ejector pins push out the end product. Then, the machine starts another cycle.
The machine keeps repeating the cycle until it produces the desired number of parts or when the molten material is over.
Variations in Injection Molding
Molding can take different variations depending on the parts' specifications. The most common types include:
-
Overmolding: this is a process that involves manufacturing plastic parts using two or more materials. For instance, it includes adding rubber to the handles to enhance grip.
-
Thermoplastic injection molding: It's the most popular type of molding, and manufacturers use it to inject thermoplastic resin into the mold, where the materials cool to form the final part.
-
Insert molding: as the name suggests, this molding involves an insert component that is placed into the mold before the resin enters. It's usually used with metallic material, which is injected and flows around the insert forming the final part.
-
Liquid silicone rubber molding: this type of molding involves the use of thermoset materials and chemical reactions to produce plastic parts.
Important Points to Note
-
Injection molding machines differ depending on size, with configurations ranging from small tabletop machines to large industrial machines for producing large parts.
-
It's to customize the process to produce parts in various shapes, sizes, textures, and colors.
-
Different factors, such as mold complexity, material, and quantity of the parts, influence the cost.
Injection molding is a complex process that involves melting the material, injecting it into a mold cavity, cooling it, and solidifying it to give a final product of a desired shape and size.


You must be logged in to post a comment.